Controllable silicon, abbreviated as SCR, is a high-power electrical component, also known as thyristor. It has the advantages of small size, high efficiency, good stability, and reliable operation. In automatic control systems, it can be used as a high-power driving device to control high-power equipment with low-power controls. Its emergence has brought semiconductor technology from the weak current field to the strong current field, becoming a component that is eagerly adopted in industries such as industry, agriculture, transportation, military research, as well as commercial and civilian electrical appliances.
One Principle diagram of thyristor operation
A thyristor has three poles - anode (A), cathode (K), and control pole (G). The core is a four layer structure composed of P-type and N-type conductors overlapping, with a total of three PN junctions. It is structurally different from a silicon rectifier diode with only one PN junction. The introduction of the four layer structure and control electrode of thyristors has laid the foundation for their excellent control characteristics of "controlling large with small".
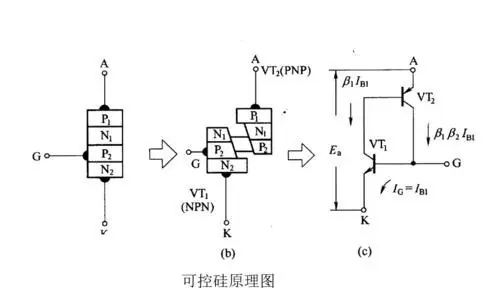
When using thyristors, as long as a small current or voltage is applied to the control electrode, a large anode current or voltage can be controlled. At present, controllable silicon components with current capacities of several hundred amperes to several thousand amperes can be manufactured. Generally, thyristors below 5 amperes are called low-power thyristors, while thyristors above 50 amperes are called high-power thyristors.
II、 What are the functions of thyristors?
One of the functions of thyristors is controllable rectification, which is also the most fundamental and important role of thyristors. The well-known diode rectifier circuit can only complete the function of rectification and does not achieve controllability. Once the diode is replaced with a thyristor, a controllable rectifier circuit is formed. In a basic single-phase half wave controllable rectification circuit, when the sine AC voltage is in the positive half cycle, only when a trigger pulse is applied to the control electrode, the thyristor is triggered to conduct, and there will be voltage output on the load. Therefore, by changing the arrival time of the trigger pulse on the control electrode, the average output voltage on the load can be further adjusted to achieve controllable rectification.
The second function of thyristor is to be used as a contactless switch, often used in automation equipment to replace general relays, with the characteristics of no noise and long service life.
The third function of thyristor is to act as a switch and voltage regulator, often used in AC circuits. Due to its different triggering times, the current passing through it is only a part of its AC cycle, and the voltage passing through it is only a part of the full voltage, thus playing a role in regulating the output voltage.
III 、Classification of thyristors
There are two types of thyristors: unidirectional thyristors and bidirectional thyristors. A bidirectional thyristor, also known as a tri terminal bidirectional thyristor, abbreviated as TRIAC. A bidirectional thyristor is structurally equivalent to two unidirectional thyristors connected in reverse, and this type of thyristor has bidirectional conductivity. Its on/off state is determined by the control pole G. Applying a positive pulse (or negative pulse) to the control electrode G can make it conduct in the positive (or negative) direction. The advantage of this device is that the control circuit is simple and there is no reverse withstand voltage problem, making it particularly suitable for use as an AC contactless switch.
Ⅳ、 What are the main parameters of thyristors?
1. Forward blocking peak voltage (VPFU)
It refers to the peak value of the forward voltage that can be repeatedly applied to the device under open circuit and forward blocking conditions of the control electrode. This voltage is set at 80% of the forward transition voltage value.
2. Reverse blocking peak voltage (VPRU)
It refers to the peak value of the reverse voltage that can be repeatedly applied to the device at the control pole open circuit and rated junction temperature. This voltage is set at 80% of the maximum reverse test voltage value.
3. Rated forward average current (IF)
At an ambient temperature of+40C, the device can conduct continuously (under standard heat dissipation conditions) through the average value of the sine half wave current of the power frequency (usually 50Hz or 60Hz, which is regulated as 50Hz in China) supplied by the power grid.
4. Positive average pressure drop (UF)
The average voltage drop between the anode and cathode when the device is subjected to the rated forward average current under specified conditions.
5. Maintain current (IH)
The minimum forward current required for the device to remain conductive when the control pole is disconnected.
6. Control electrode trigger current (Ig)
The minimum control electrode DC current required to fully conduct the thyristor when a DC voltage of 6V is applied between the anode and cathode.
7. Trigger voltage of control electrode (Ug)
It refers to the minimum DC voltage applied to the control electrode when transitioning from a blocking state to a conducting state.







